Understanding the present simple
/So what is the present simple and when do we use it?Ok let’s start off by looking at the USE.
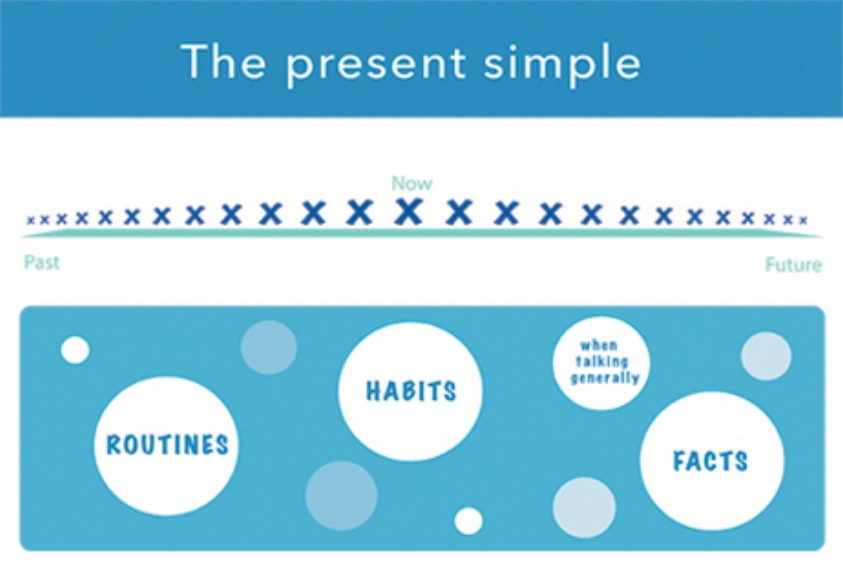
We use this tense when we are talking about:
Routines, habits, facts and when talking generally about things.
This probably still sounds a bit vague so let’s look at these one by one.
ROUTINES
This refers to what we usually do and particularly when we do them repeatedly,
at a certain time every day. Here are some of my routines:
I buy a travel card every Monday
I get up at 7am
I brush my teeth before going to bed
HABITS
Habits are similar to routines but less about our schedule. People have good or
bad habits that they often do without thinking about and can’t stop. Here are some
of my good and bad habits (!):
I exercise regularly
I don’t put things away after I’ve used them
I don’t smoke
I often leave things until the last minute
FACTS
Here are some facts about the UK:
If you live until 100, you get a personalised card from the queen!
Buckingham Palace has its own police station!
The English drink more tea than anyone else in the world (not so surprising!)
WHEN TALKING GENERALLY
These things don’t always happen but they are generally true.
The sun shines in summer
Children learn at school
People relax at weekends
In the infographic below you can see on the time line that the present
simple can be true now, in the past and in the future. If you look at the
example sentences above, they aren’t just referring to today or this current time.
We often use these adverbs with the present simple:
ALWAYS, OFTEN, SOMETIMES, NOT USUALLY and NEVER.
There are also more but these are the most common. You can see from
the infographic how these adverbs are used with always at the top to convey
high frequency and never at the bottom with 0 frequency.
Now let’s look at the form of the present simple. The positive form of I, you,
we you (plural) and they is easy as we just add the infinitive (the verb).
Here are some examples,
I eat, you eat, we eat, you eat, they eat I go, you go, we go, you, go they go
I drink, you drink, we drink, you drink, they drink
If you are using he, she and it, you need to remember to add an S.
For example,
Here are some examples (about my brother and sisters). All true!
Lucy (she) loves reading
Daniel (he) goes surfing.
Miranda (she) has a little boy
Nell (she) speaks Chinese
If the verb ends with sh, ch or x, you need to add -es
For example:
He watches, she watches, it watches
He washes, she washes, it washes
He fixes, she fixes, it fixes
If the verb ending with a consonant followed by a y, you need to add -ies
For example:
He flies, she flies, it flies
He marries, she marries, it marries(!)
If the verb ends with an o, we add es
For example:
He goes, she goes, it goes
He does , she does, it does
Remember that the verb TO BE has different rules and is not part of this tense.
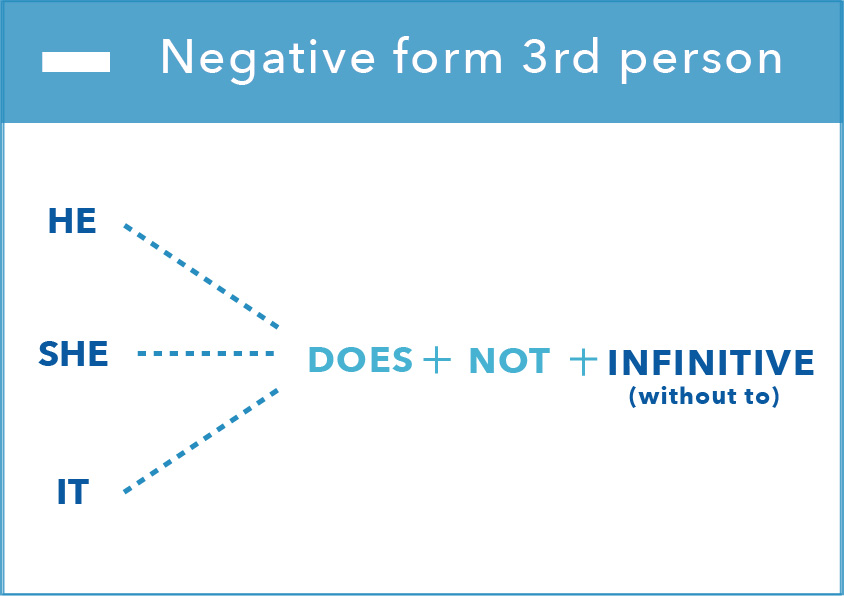
The infographic below shows how to form the negative with I, you,
we, you and they. We usually contract DO NOT to don’t.
Here are some examples:
I don’t have a car
We don’t live in the countryside
My sisters (they) don’t have short hair
If you are talking about he, she or it in negative, you need to add DOES NOT.
The S moves from the verb to the auxilary DO. We usually contract this and
say doesn’t.
Here are some examples:
Lucy doesn't live in South London
Daniel doesn’t have blue eys
Miranda doesn’t have brown hair
Nell doesn’t have a car
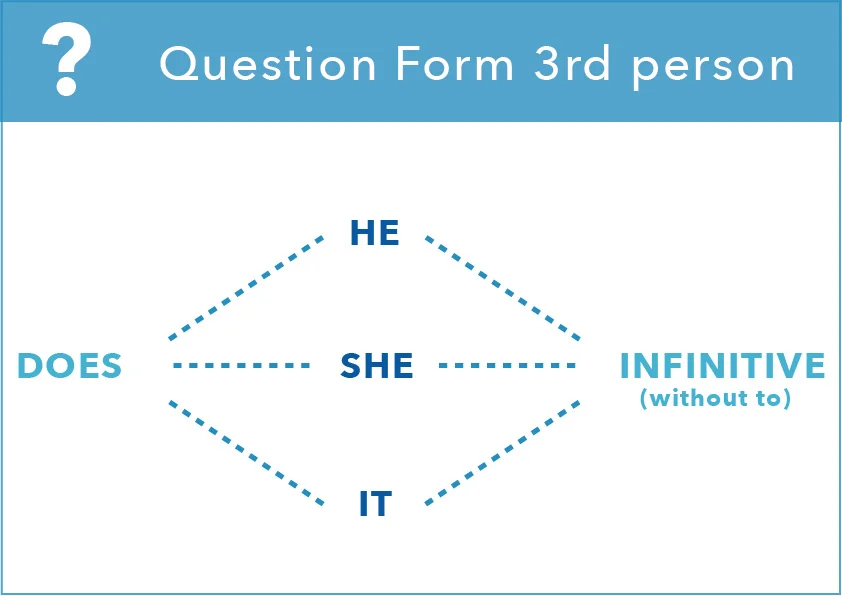
When you ask questions in the present simple, the subject and auxilary DO
are inverted. The DO comes at the beginning and is followed by I, you, we,
you (plural) and they and the subject is followed by the infinitive(the verb).
For example:
Do you live in London?
Do you eat meat?
Do you speak English?
If you are asking a question with he, she or it, you just need to put DOES at the
beginning, instead of DO.
For example:
Does he live in London?
Does he eat cheese?
Does he work full-time?